Arduino演習Communication/SerialCallResponse用スケッチは以下となります。
//SerialCallResponse
// This example code is in the public domain.
import processing.serial.*;
int bgcolor; // Background color
int fgcolor; // Fill color
Serial myPort; // The serial port
int[] serialInArray = new int[3]; // Where we'll put what we receive
int serialCount = 0; // A count of how many bytes we receive
int xpos, ypos; // Starting position of the ball
boolean firstContact = false; // Whether we've heard from the microcontroller
void setup() {
size(256, 256); // Stage size
noStroke(); // No border on the next thing drawn
// Set the starting position of the ball (middle of the stage)
xpos = width/2;
ypos = height/2;
// Print a list of the serial ports for debugging purposes
// if using Processing 2.1 or later, use Serial.printArray()
println(Serial.list());
// I know that the first port in the serial list on my mac
// is always my FTDI adaptor, so I open Serial.list()[0].
// On Windows machines, this generally opens COM1.
// Open whatever port is the one you're using.
String portName = Serial.list()[4];
myPort = new Serial(this, portName, 9600);
}
void draw() {
background(bgcolor);
fill(fgcolor);
// Draw the shape
ellipse(xpos, ypos, 20, 20);
}
void serialEvent(Serial myPort) {
// read a byte from the serial port:
int inByte = myPort.read();
// if this is the first byte received, and it's an A,
// clear the serial buffer and note that you've
// had first contact from the microcontroller.
// Otherwise, add the incoming byte to the array:
if (firstContact == false) {
if (inByte == 'A') {
myPort.clear(); // clear the serial port buffer
firstContact = true; // you've had first contact from the microcontroller
myPort.write('A'); // ask for more
}
}
else {
// Add the latest byte from the serial port to array:
serialInArray[serialCount] = inByte;
serialCount++;
// If we have 3 bytes:
if (serialCount > 2 ) {
xpos = serialInArray[0];
ypos = serialInArray[1];
fgcolor = serialInArray[2];
// print the values (for debugging purposes only):
println(xpos + "\t" + ypos + "\t" + fgcolor);
// Send a capital A to request new sensor readings:
myPort.write('A');
// Reset serialCount:
serialCount = 0;
}
}
}
(1)PArduino演習Communication/SerialCallResponse用スケッチを実行するとコンソールに
COM1 COM3 COM4 COM5 COM10
と表示されます。
(2)Arduinoと接続のポートはいつもCOM10であり、port = new Serial(this, Serial.list()[4], 9600);とするとつながります。
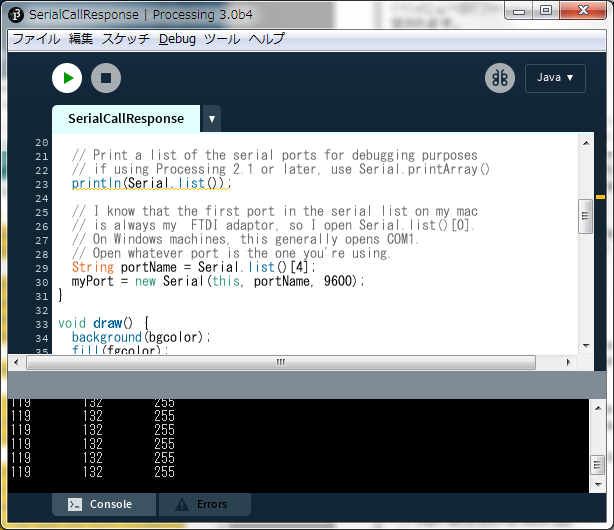
(3)コンソールには、X位置とY位置とスイッチのON/OFFが表示されます。
(4)スイッチのONのときコンソール画面は以下のようになります。
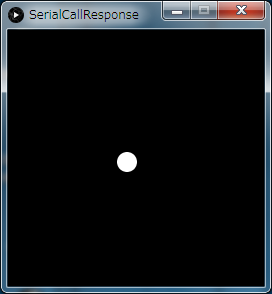
(5)スイッチがONの時の実行画面は以下のようになります。
(1)トラブルなく、動作も安定しています。
(2)起動時のみArduinoからコード'A'が送信されます。
(3)パソコン側では、'A'を受信したら受信バッファを初期化します。
(4)パソコン側で受信可能となったら、コード'A'を送信します。
(5)Arduino側でコード'A'を受信したら、X値、Y値、ON/OFFのデータを送信します。
(6)こうすると受信処理が確実に実行できそうです。