40章:Arduino演習(HC-SR04 超音波距離センサーモジュール編)
http://skomo.o.oo7.jp/f47/hp47_40.htm
Arduino UNOとESP-WROOM-02はHC-SR04 超音波距離センサーモジュール制御において、互換性があります。ただし、ESP-WROOM-02のシリアル 通信のボ−レートは115200bpsに設定する必要があります。
HC-SR04 超音波距離センサー制御回路図を以下に示します。
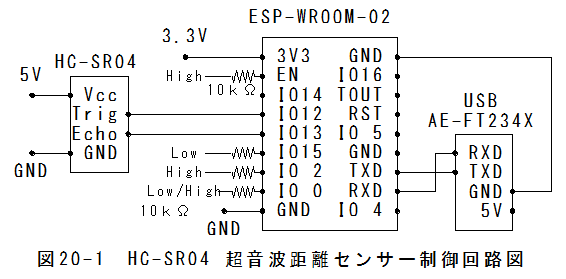
(1)const int pingPin = 12;//**7→12に変更
(2)const int inPin = 13;//**8→13変更
(3)Serial.begin(9600);→Serial.begin(115200);に変更変更します。**注
(4)delay(1000);//**100→1000に変更
/*
HC-SR04
Ping))) Sensor
This sketch reads a PING))) ultrasonic rangefinder and returns the
distance to the closest object in range. To do this, it sends a pulse
to the sensor to initiate a reading, then listens for a pulse
to return. The length of the returning pulse is proportional to
the distance of the object from the sensor.
The circuit:
* +V connection of the PING))) attached to +5V
* GND connection of the PING))) attached to ground
* SIG connection of the PING))) attached to digital pin 7
http://www.arduino.cc/en/Tutorial/Ping
created 3 Nov 2008
by David A. Mellis
modified 30 Aug 2011
by Tom Igoe
This example code is in the public domain.
*/
// this constant won't change. It's the pin number
// of the sensor's output:
const int pingPin = 12;//**変更
const int inPin = 13;//**変更
void setup() {
// initialize serial communication:
Serial.begin(115200);//**変更
}
void loop()
{
// establish variables for duration of the ping,
// and the distance result in inches and centimeters:
long duration, inches, cm;
// The PING))) is triggered by a HIGH pulse of 2 or more microseconds.
// Give a short LOW pulse beforehand to ensure a clean HIGH pulse:
pinMode(pingPin, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(pingPin, LOW);
delayMicroseconds(2);
digitalWrite(pingPin, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(10);
digitalWrite(pingPin, LOW);
// The same pin is used to read the signal from the PING))): a HIGH
// pulse whose duration is the time (in microseconds) from the sending
// of the ping to the reception of its echo off of an object.
pinMode(inPin,INPUT);
duration = pulseIn(inPin, HIGH);
// convert the time into a distance
inches = microsecondsToInches(duration);
cm = microsecondsToCentimeters(duration);
Serial.print(inches);
Serial.print("in, ");
Serial.print(cm);
Serial.print("cm");
Serial.println();
delay(1000);//**変更
}
long microsecondsToInches(long microseconds)
{
// According to Parallax's datasheet for the PING))), there are
// 73.746 microseconds per inch (i.e. sound travels at 1130 feet per
// second). This gives the distance travelled by the ping, outbound
// and return, so we divide by 2 to get the distance of the obstacle.
// See: http://www.parallax.com/dl/docs/prod/acc/28015-PING-v1.3.pdf
return microseconds / 74 / 2;
}
long microsecondsToCentimeters(long microseconds)
{
// The speed of sound is 340 m/s or 29 microseconds per centimeter.
// The ping travels out and back, so to find the distance of the
// object we take half of the distance travelled.
return microseconds / 29 / 2;
}
(1)ESP-WROOM-02のフラッシュ書き換え時のピン設定
*ENピン:(Chip Enable.)→High(10kΩプルアップ)
*GPIO-15ピン:(Type I/O MTDO;HSPI_CS; UART0_RTS)→LowHigh(10kΩプルダウン)
*GPIO-2ピン:(Type I/O UART Tx during flash programming)→High(10kΩプルアップ)
*GPIO-0ピン:(Type I/O SPI_CS2)→Low(10kΩプルダウン)(Lowでラッシュ書き換えモード)
*TXピン:USBシリアル変換モジュールのRX
*RXピン:USBシリアル変換モジュールのTX
*GNDピン:USBシリアル変換モジュールのGND
(2)ESP-WROOM-02の電源を投入します。
(3)メニュー「ツール」_「ポート」_「COM14」を選択します。
(4)メニュー「スケッチ」_「マイコンボードに書込む」を選択します。
(5)書込みが完了します。
(6)GPIO-0ピン:(Type I/O SPI_CS2)→High(10kΩプルアップ)に戻します。
(7)ESP-WROOM-02の電源を再投入します。
(1)arduino.exeを起動して、シリアルモニタを開きます。
(2)GPIO-0ピン:(Type I/O SPI_CS2)→High(10kΩプルアップ)に戻し、ESP-WROOM-02の電源を再投入します。
(3)シリアルモニタの受信データを以下に示します。
33in, 86cm 33in, 86cm 33in, 85cm 33in, 85cm 33in, 85cm 33in, 85cm 33in, 85cm 33in, 86cm 33in, 86cm 33in, 86cm 33in, 86cm 33in, 86cm 33in, 85cm 33in, 86cm 33in, 85cm 33in, 85cm 33in, 85cm 33in, 86cm 33in, 85cm 33in, 86cm 33in, 86cm 33in, 85cm 33in, 85cm 33in, 85cm 33in, 85cm
(1)Arduino UNOとESP-WROOM-02はHC-SR04 超音波距離センサー制御において、互換性があります。
(2)ただし、ESP-WROOM-02のシリアル通信のボ−レートは115200bpsに設定する必要があります。